Bible Background & History
Background, historical and cultural information to help you study the bible.
Bible Study Background & History

Sheep in Scripture
Metaphors about sheep and their shepherd have a rich background in the Old Testament that continues in the New Testament. Without a shepherd, sheep can easily end up hungry, lost and the victim of predators.

Overview of Biblical History
Whenever you study Scripture, it’s important to know where your particular passage fits into biblical history. As Karl Barth said: “The Bible is not a philosophical book, but a history book, the book of God’s mighty acts, in which God becomes knowable to us.” Here’s a simple overview of biblical history.

Empires of the Ancient World
Over the course of biblical history, the children of Israel were challenged, threatened and conquered by several other ancient empires. Understanding something about those empires can inform your biblical understanding.

How the Apostles died
Scripture records the deaths of only 2 apostles: James (Acts 12:1-2) and Judas Iscariot (Matthew 27:5). Most of what we know about the deaths of the other apostles comes from early Christian writers and church tradition. Most scholars think the Apostle John is the only apostle who died of natural causes. The exact dates are unknown, most are estimates.

Israel’s 3 Temples
Israel had 3 temples during its Old & New Testament time period. The original temple was built by Solomon. After the exile, a second temple was built under Zerubbabel. Finally, Herod the Great expanded and enlarged the temple during his reign.

Kings of Persia in Biblical Times
A list of the Kings of Persia in biblical times and where they appear in Scripture.
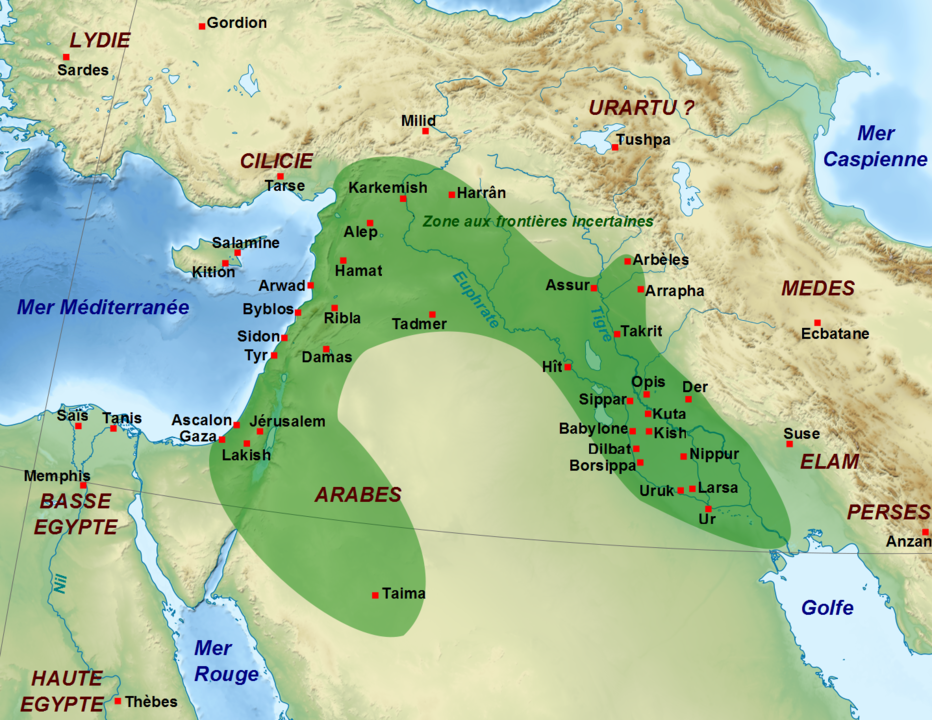
Kings of Babylon in Biblical times
The Babylonian Empire became a world power in 625 BC after the fall of Assyria. Babylon continued its reign until 536 BC. Nebuchadnezzar, its greatest king, reigned in the days of Daniel and took the southern Kingdom of Judah into captivity after the fall of Jerusalem in 586 BC. Babylon was finally captured by the Medes and Persians under Cyrus as predicted by the prophet Daniel, and the Babylonian Empire came to an end in 536 BC.

Jewish Day (1st Century) explained
What does the first watch mean? What is the “third hour”? The Jewish day ran from sunset to sunset and was divided in 8 equal parts called watches and hours. Here’s what they mean.

Kings of Assyria in Biblical times
The Assyrian Empire is important to biblical history for devastation the kingdom of Israel and taking the 10 northern tribes into captivity in 722 BC.

Geography of the New Testament
Geography of the New Testament: Learn the important cities, regions, provinces, and lakes of New Testament Israel from Wednesday in the Word.

New Testament Priesthood
These are the principal religious and political offices in Judaism at the time of Jesus.

New Testament History from Alexander to Titus
When the Old Testament ends, Israel is under control of the Persian empire. When the New Testament begins, Israel is under Roman control. The switch occurred because of Alexander the Great. This historical background helps explain the political situation at the time of the New Testament.

Chronological List of OT Prophets
Chronological list of Old Testament prophets: see when they ministered, which kings where in power and who their contemporary prophets were.

Weights and measures of the Bible
Ever wondered what a cubit is? When is the third watch? How much is a denarius, an omer or a talent? Here’s a chart of time, weights and measures found in Scripture and how to convert them.

Coins in the Bible
What’s the difference between a shekel, a denarius, and a talent? They are all coins circulating at the time of the New Testament. But one was Jewish, one Greek, and one Roman. Here’s what they were worth in relation to each other.

What was the Canaanite religion?
“Canaanite” refers to the group of polytheistic people living in the historical region of Israel and Palestine at the time of the Old Testament. Canaanite mythology centered around three primary exploits of Baal.

Introduction to Ancient Egypt
The first third of the book of Exodus takes place in Egypt. The Israelites had lived in Egypt for 400 years and were steeped in Egyptian culture. The cultural and historical setting of Exodus is ancient Egypt. Here’s a brief introduction.

Introduction to the Intertestamental Period
The time between the end of the Old Testament (400BC from the prophet Malachi) to the preaching of John the Baptist (25 AD) is known as the “intertestamental” period. Here’s an overview of what happened.

When did the Exodus happen?
When it comes to biblical history, you can divide scholars into minimalists and maximalists. Minimalists believe almost nothing in the Old Testament is historically accurate. Maximalists believe the Old Testament is a reasonably accurate historical document. Among the maximalists, there are two main competing theories about the date of the Exodus: early and late.

Introduction to the Northern Kingdom
After the death of King Solomon, two of his sons, Rehoboam and Jeroboam, fought for the throne. When Rehoboam harshly raised taxes on the people, the 10 northern tribes rebelled and installed Jeroboam as their king, creating the northern kingdom of Israel. The two southern tribes, Benjamin and Judah, remained with Rehoboam and became the kingdom of Judah.

Introduction to the Southern Kingdom
After the death of King Solomon, two of his sons, Rehoboam and Jeroboam, fought for the throne. When Rehoboam harshly raised taxes on the people, the 10 northern tribes rebelled and installed Jeroboam as their king, creating the northern kingdom of Israel. The two southern tribes, Benjamin and Judah, remained with Rehoboam and became the kingdom of Judah.

Introduction to the Exile and Return
The period of the divided kingdom ended with the people of Israel being taken into captivity. First, the people of the northern kingdom were conquered by Assyria, leaving Judah to struggle on alone. Finally, the southern kingdom of Judah was conquered by the Babylonians, leaving all the children of Israel in exile from the land. Here is an overview and timeline of the exile of Israel and her return from captivity.
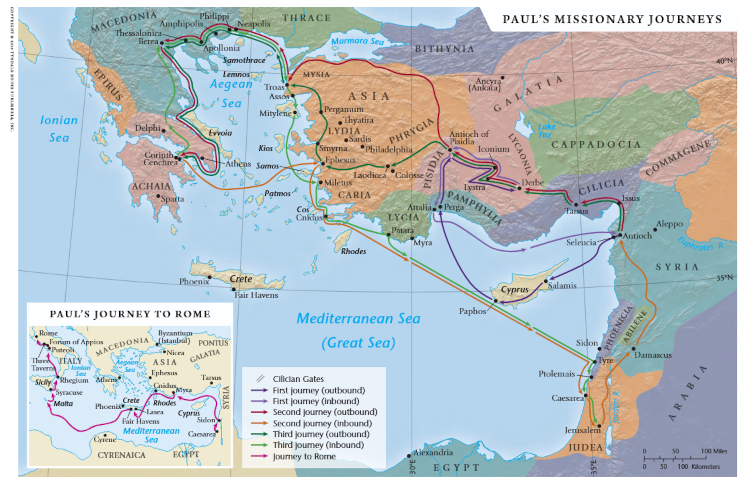
Paul’s Missionary Journeys
The itinerary of Paul’s three missionary journeys on 1 map and in 1 chart with links to background information on the cities and the reference in Acts.

How many letters did Paul write to Corinth?
How many letters did the Apostle Paul write to the Corinthian church? The answer is not as easy as it sounds. We have two letters to the church at Corinth in our Bible, but both of these letters mention another letter. Many scholars believe Paul wrote four letters to the Corinthian church but only two of them survived. If they are right, the chronology of Paul’s correspondence and visits to Corinth might look something like this.

City of Corinth
In Paul’s time Corinth was the 2nd most important city in the Roman empire. Corinth was an exceptionally wealthy and important city in Greece.

Early Church Heresies
While not a complete list of early church heresies, these groups are the ones that the New Testament authors seem to write against and respond to most often.

Ezra-Nehemiah Chronology
Chronology of the post exile: Ezra-Nehemiah

Chronology of Paul
A timeline of the major events in the life of the Apostle Paul and the dating of his letters.

Jeremiah’s Ministry Chronology
Jeremiah was a prophet to the southern kingdom of Judah who wrote the book of Jeremiah. His name means “exaltation of the Lord.” Below is a basic chronology of his 40+ year ministry.

Kings of Israel and Judah
This chart summarizes the Kings of Israel and Judah from the crowning of Saul to the captivity of Judah.

Hebrew Calendar explained
When studying the Old Testament, dates can be a source of confusion, especially when they switch between the Jewish name and the Babylonian name in the same story. Here are my reference tables.
Top Banner photo by Giammarco Boscaro on Unsplash

